Revolutionizing Retail
Unleashing the Power of AI Tools for Dynamic Supply Chain Visibility and Optimization
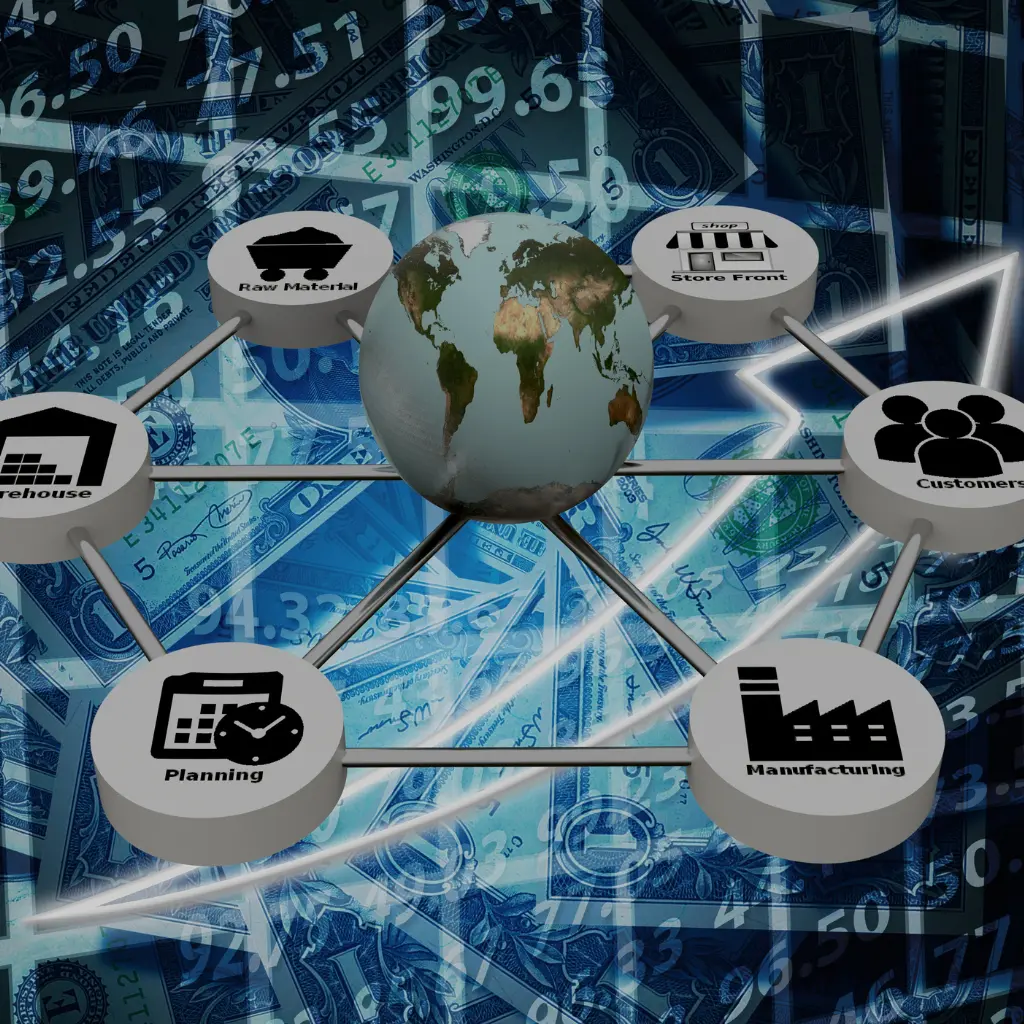
This article delves into the intricate world of Retail B2C Industry AI Tools designed for Supply Chain Visibility and Optimization. From algorithmic Supplier Risk Management to real-time Transportation Route Optimization, each tool in this comprehensive set plays a vital role in reshaping how businesses manage and streamline their supply chains.
In the fast-paced realm of Retail B2C, integrating cutting-edge technology is pivotal for staying ahead in a competitive landscape.
As we explore the technical nuances, the training needs of existing staff, and the challenges faced in creating and adopting these tools, a clearer picture emerges of AI’s potential impact and transformative power in revolutionizing supply chain dynamics.
Join us on a journey through the complexities, costs, benefits, and future possibilities of Retail B2C Industry AI Tools.
Table of Contents
AI Tool ideas
Supply Chain Visibility and Optimization Platform:
- Centralized dashboard for end-to-end visibility.
- Integration with ERP systems for comprehensive data access.
- Real-time analytics for decision-making.
- Customizable reporting for different stakeholders.
AI-Powered Supplier Risk Management:
- Implement machine learning algorithms for risk assessment.
- Integration with third-party databases for supplier information.
- Automated alerts for potential risks based on continuous monitoring.
- Recommendations for risk mitigation strategies.
- Historical data analysis for predicting future risks.
Transportation Route Optimization:
- Real-time integration with traffic and weather APIs.
- Machine learning algorithms for route optimization considering cost and time.
- Continuous monitoring and dynamic route adjustments.
- Historical data analysis to improve future route planning.
Warehouse Management Automation:
- Integration with Warehouse Management Systems (WMS).
- AI-driven tools for demand forecasting to optimize inventory levels.
- Order fulfilment optimization for minimizing lead times.
- Logistics optimization for efficient product movement within the warehouse.
- Real-time monitoring of inventory levels and order status.
Reverse Logistics Optimization:
- Algorithms for optimizing return processes and reducing costs.
- Integration with inventory systems to manage returned items.
- Automation of return logistics for faster processing.
- Customer support integration for streamlined communication.
Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency:
- Implementation of blockchain for secure and transparent data sharing.
- Integration with all nodes of the supply chain for end-to-end visibility.
- Real-time tracking and traceability of products.
- Smart contracts for automating transactions and agreements.
Business Knowledge Requirements
Consumer Behavior Analysis:
Delving into consumer behaviour patterns is imperative to optimize supply chain visibility. This entails studying purchasing habits, preferences, and trends. Analyzing the factors influencing buying decisions, such as seasonality and promotional events, aids in forecasting demand accurately. This knowledge forms the basis for developing AI algorithms that enhance inventory management and order fulfilment.
Supplier Relationships and Dynamics:
In the retail B2C realm, establishing and maintaining robust supplier relationships is pivotal. Understanding the intricacies of supplier networks, negotiation processes, and the impact of supplier performance on the overall supply chain is essential. This knowledge contributes to developing AI-driven Supplier Risk Management tools, ensuring the mitigation of potential disruptions in the supply chain.
Logistics and Transportation Insights:
A grasp of logistics and transportation intricacies is vital for effective route optimization. This involves understanding the various modes of transportation, real-time factors like traffic and weather impact, and the cost implications of different routes. Integrating this knowledge into AI algorithms facilitates the creation of tools that optimize transportation routes for cost-efficiency and timely delivery.
Warehouse Operations Understanding:
Developing tools for Warehouse Management Automation necessitates an in-depth understanding of warehouse operations. This includes familiarity with inventory management, order fulfilment processes, and logistics within the warehouse. AI tools must align with the day-to-day challenges faced in warehouses, ensuring seamless integration with existing Warehouse Management Systems.
Returns Management and Customer Service:
In the B2C sector, returns management is a critical aspect that directly impacts customer satisfaction. Understanding the intricacies of the return process, including reasons for returns and customer support dynamics, is essential. Integrating this knowledge into AI algorithms enables the automation of reverse logistics, minimizing costs and enhancing customer experience.
Data Security and Compliance Awareness:
Lastly, recognizing the importance of data security and compliance within the retail industry is paramount. Retailers deal with sensitive customer information and must comply with data protection regulations. Embedding robust security measures into AI tools ensures the confidentiality and integrity of the data, fostering trust with both consumers and regulatory bodies.
Technical Knowledge Requirements
Programming Languages and Development Tools:
A solid foundation in programming languages is indispensable to embark on developing Retail B2C Industry AI Tools. Python, Java, or C++ proficiency is essential for building the core algorithms and functionalities. With its extensive libraries and frameworks, Python is often a go-to language for AI and machine learning applications.
Data Science and Machine Learning Expertise:
It’s essential to thoroughly comprehend data science and machine learning concepts, which involve understanding statistical modelling, predictive analytics, and machine learning algorithms. Knowing popular machine learning libraries like TensorFlow or PyTorch is essential for developing AI-powered features like risk assessment algorithms and route optimization.
Database Management:
A robust knowledge of database management systems is vital for handling vast amounts of data in the supply chain. It is essential to have proficiency in relational databases such as MySQL or PostgreSQL and NoSQL databases like MongoDB. Effective data management is pivotal for real-time monitoring and reporting features.
API Integration Skills:
Since these tools involve real-time data from external sources, the ability to integrate with various APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) is a critical technical requirement. This includes incorporating supplier databases, traffic and weather APIs for transportation route optimization, and other external systems. Familiarity with tools like Postman or Swagger is beneficial for API testing and documentation.
Cloud Computing Platforms:
Utilizing cloud computing platforms such as AWS (Amazon Web Services), Azure, or Google Cloud is crucial for scalable and flexible solutions. Understanding cloud infrastructure, storage, and services is essential for hosting and deploying AI tools. Cloud platforms offer the computational power necessary for complex algorithms and real-time data processing.
Blockchain Development Knowledge:
A foundational understanding of blockchain technology is required to implement blockchain in supply chain transparency. Proficiency in blockchain development platforms like Ethereum or Hyperledger is necessary. Knowledge of intelligent contracts, consensus algorithms, and decentralized applications (DApps) contributes to creating a secure and transparent data-sharing system.
User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) Design:
Developing a user-friendly interface is vital for tool adoption. Knowledge of UI/UX design principles and proficiency in front-end development technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript is essential. Using frameworks like React or Angular can enhance the development of intuitive and visually appealing dashboards.
Security Measures and Compliance:
Understanding cybersecurity principles is imperative to ensure the security of sensitive data. Knowledge of encryption techniques, secure data transmission, and adherence to compliance standards such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) is crucial. Implementing secure coding practices safeguards the AI tools against potential vulnerabilities.
Mobile and Cross-Platform Development:
Consideration for mobile accessibility may be necessary. Knowledge of mobile development languages like Swift (for iOS) or Kotlin (for Android) or cross-platform frameworks like Flutter or React Native ensures that the AI tools can be accessed and utilized on various devices, enhancing their versatility.
Current AI Tools and Technologies available for Supply Chain Visibility and Optimization
Advanced Analytics and AI Platforms:
We can find several advanced analytics and AI platforms to build Retail B2C Industry AI Tools for Supply Chain Visibility and Optimization. Platforms such as IBM Watson, Microsoft Azure AI, and Google Cloud AI offer pre-built machine learning models and tools that streamline the development of AI-powered features like demand forecasting, route optimization, and risk management.
Blockchain Platforms for Supply Chain:
Blockchain technology is gaining traction for enhancing transparency in the supply chain. Platforms like IBM Blockchain and Hyperledger Fabric provide robust frameworks for implementing blockchain solutions. These platforms offer features like smart contracts, decentralized consensus, and secure data sharing, ensuring the integrity and traceability of the entire supply chain.
Real-Time Data Integration Platforms:
Platforms like Apache Kafka or Amazon Kinesis can be employed to facilitate real-time data integration from various sources. These platforms enable the seamless streaming and processing of data, supporting functionalities like real-time monitoring and adaptation to changing conditions in transportation route optimization and warehouse management.
Transportation Management Systems (TMS):
Transportation Management Systems, such as Oracle Transportation Management and SAP Transportation Management, are already prevalent in the market. These systems provide tools for optimizing transportation routes based on cost, time, and real-time data. Integrating such systems into AI tools enhances the efficiency of transportation route optimization algorithms.
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS):
For Warehouse Management Automation, existing WMS solutions like Manhattan Associates and JDA Warehouse Management are widely used. These systems offer features for inventory optimization, order fulfilment, and logistics within warehouses. Integration with these systems streamlines the development of AI-driven tools for warehouse management.
Supply Chain Visibility Platforms:
Dedicated supply chain visibility platforms like E2open and Control Tower by Elemica provide end-to-end visibility into supply chain operations. These platforms often include features like real-time tracking, analytics, and reporting. Integrating with such platforms can enhance AI tools’ overall visibility and analytics capabilities.
AI-Powered Supplier Risk Management Solutions:
Specialized solutions for AI-powered supplier risk management, such as Resilinc and RiskMethods, are available in the market. These tools leverage machine learning algorithms to assess and monitor supplier risks. Integrating these solutions can enhance the AI toolset’s capabilities for automated alerts, risk assessment, and recommendations for risk mitigation.
Route Optimization Software:
Dedicated route optimization software, including tools like Route4Me and OptimoRoute, is readily available. These solutions offer algorithms for optimizing routes based on cost and time. Integration with such software streamlines the development of Transportation Route Optimization tools, ensuring efficient and dynamic route planning.
Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) Platforms:
You can use Microsoft Azure Blockchain and AWS Blockchain Templates to implement blockchain without the complexity of building a network from scratch. These are blockchain-as-a-service platforms that make implementation easier. These platforms provide pre-configured blockchain environments, making it easier to integrate blockchain for secure and transparent data sharing in the supply chain.
Training Needs for Staff Managing AI Tools
Understanding the AI Toolset:
To train our current staff on AI tools for supply chain optimization in the Retail B2C Industry, we must start by ensuring they understand the toolset. This means we must familiarize employees with each tool, what it does, and how it can help optimize supply chain operations. We can conduct workshops or training sessions to help our staff grasp these tools’ capabilities and contributions.
Technical Training for System Navigation:
Since the AI tools involve complex algorithms and interfaces, staff members need technical training to navigate and use the system effectively. This includes training to access dashboards, input data, interpret analytics, and execute specific functions within the toolset. Hands-on sessions and simulations can be valuable in building practical skills.
Data Input and Maintenance Training:
Data input and maintenance staff require specialized training on the procedures for entering and managing data within the AI tools. This involves understanding data formats, ensuring data accuracy, and complying with data governance policies. Training programs should cover data input best practices and how accurate data contributes to the effectiveness of the tools.
Interpreting Analytics and Reports:
Given the AI toolset’s emphasis on real-time monitoring and reporting, staff members need training on interpreting analytics and reports generated by the tools. Customized training sessions can help businesses make informed decisions based on valuable insights and patterns displayed in the dashboard. This knowledge is crucial for leveraging the tools to their full potential.
Supplier Risk Management and Route Optimization Workshops:
Specialized workshops on supplier risk management and route optimization can benefit supplier relationship management and logistics staff. These sessions can delve into the specific algorithms and methodologies the tools employ in these areas.
Warehouse Management and Reverse Logistics Training:
Employees responsible for warehouse operations and reverse logistics need targeted training on AI-driven Warehouse Management Automation and Reverse Logistics Optimization tools. This training should cover inventory optimization strategies, order fulfilment processes, and the automation of return logistics. Practical training sessions within the warehouse environment can enhance understanding and application.
Security and Compliance Training:
Given the sensitive nature of the data involved in supply chain operations, staff members should receive training on security measures and compliance requirements. This includes understanding how to protect sensitive information, recognizing potential security threats, and adhering to industry regulations such as GDPR.
Troubleshooting and Support Training:
Staff members should undergo training on troubleshooting procedures and support mechanisms to address potential technical issues and challenges. This includes understanding common issues, utilizing support resources, and communicating technical concerns to the IT or support team. Training on logging and tracking issues within the AI toolset ensures a swift resolution of problems.
Continuous Learning and Updates:
The field of AI and supply chain management is dynamic, with continuous advancements and updates. Establishing a culture of constant learning is essential. Providing access to learning resources, webinars, and updates on the latest features or enhancements in the AI toolset ensures that staff members stay abreast of industry trends and maximize the tools’ evolving capabilities.
Technical Integrations Requirements
ERP System Integration:
After building Retail B2C Industry AI Tools, one crucial technical integration is with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. Integrating with ERP systems, such as SAP or Oracle, ensures seamless access to critical business data. This integration enhances the efficiency of the toolset by providing a holistic view of operations, allowing for better decision-making and coordination across various business functions.
Supplier Databases and Risk Assessment Tools:
To empower AI-Powered Supplier Risk Management, integration with external supplier databases and risk assessment tools is essential. Connecting the AI tools to comprehensive databases and risk evaluation platforms, possibly through APIs, ensures real-time access to supplier information. This integration facilitates automated risk assessments, alert systems, and proactive risk mitigation strategies based on the latest data.
Traffic and Weather Data APIs:
Integration with real-time traffic and weather data is critical for Transportation Route Optimization. Leveraging APIs from providers like Google Maps or The Weather Channel enables the tool to monitor and adapt routes continuously based on current conditions. This integration enhances the accuracy of route optimization algorithms, ensuring timely and cost-effective deliveries.
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS):
Integrating the AI toolset with Warehouse Management Systems is vital for Warehouse Management Automation. This ensures synchronization between the AI-driven tools and the warehouse operations. Real-time updates on inventory levels, order fulfilment, and logistics within the warehouse are crucial for optimizing these processes efficiently.
Inventory and Customer Support Systems for Reverse Logistics:
Integration with inventory and customer support systems is imperative to optimize the reverse logistics process. Linking the AI tools with inventory databases and customer support platforms ensures seamless automation of the return process. This integration enhances the visibility and efficiency of handling returned items, reducing costs and improving customer satisfaction.
Blockchain Integration Across the Supply Chain:
Integration across the entire supply chain ecosystem is necessary to implement Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency. This involves connecting the blockchain-based toolset with suppliers, manufacturers, logistics partners, and retailers. Blockchain integration ensures secure and transparent data sharing, providing real-time visibility and traceability for all stakeholders involved in the supply chain.
APIs for Data Sharing and Integration:
To facilitate data sharing and integration with external systems, creating Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) is essential. Designing APIs allows the AI toolset to communicate seamlessly with other tools, platforms, and databases. This extensibility ensures that AI tools adapt to changing business requirements and integrate with emerging technologies.
Real-time Monitoring and Reporting Systems:
Integration with real-time monitoring and reporting systems is crucial to provide stakeholders with up-to-the-minute insights. Linking the AI toolset with reporting platforms, dashboards, or analytics tools ensures decision-makers can access timely and accurate information. This integration enables proactive decision-making based on the latest data trends.
User Authentication and Access Management:
Implementing robust user authentication and access management systems is necessary to control who can access and modify data within the AI toolset. Integration with authentication systems, like OAuth or LDAP, ensures secure access for authorized personnel while safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized users.

Arindam Roy
An Automation Consultant with 25+ years of IT Experience
Challenges and Workarounds on AI Tools for Supply Chain Visibility and Optimization
Integration Complexity
Challenge:
Integrating AI tools with existing systems, such as ERP, WMS, and external databases, can be complex due to varying data structures and formats. Ensuring seamless communication between these diverse systems requires careful planning and technical expertise.
Workaround:
Adopt standardized data formats and utilize middleware solutions that act as intermediaries, facilitating smooth communication between different systems. Establish well-documented APIs for easy integration and conduct thorough testing during the integration phase to identify and address potential issues.
Data Quality and Accuracy
Challenge:
The effectiveness of AI tools heavily relies on the quality and accuracy of the data input. Only accurate or complete data can lead to good analytics, impacting decision-making and overall supply chain performance.
Workaround:
Implement robust data governance practices to maintain data quality. Conducted regular audits, established data validation checks, and provided training to ensure staff members input accurate and relevant information. Employ data cleansing techniques and algorithms to identify and rectify inconsistencies.
User Adoption and Training
Challenge:
Introducing AI tools may be resistant to staff unfamiliar with the technology. The complexity of the tools and the need for specialized training can pose challenges regarding user adoption.
Workaround:
- Prioritize user-friendly design and conduct comprehensive training programs.
- Emphasize the benefits of the tools in terms of efficiency gains, improved decision-making, and overall supply chain optimization.
- Provide ongoing support and encourage a culture of continuous learning to boost user confidence.
Security Concerns
Challenge:
When we handle sensitive data in our supply chain, security concerns come up. To ensure transparency and secure data sharing, we can integrate blockchain technology. However, we need to ensure that we have robust security measures to prevent potential breaches.
Workaround:
- Implement encryption protocols and secure authentication mechanisms and regularly update security measures.
- It is essential to adhere to the regulations and standards set by the industry to ensure the privacy of data.
- Regularly conducting comprehensive security audits to identify potential vulnerabilities and quickly addressing them is critical for ensuring the security of your valuable systems and data.
Costs and ROI Calculation
Challenge:
Implementing AI tools involves initial development, integration, and training costs. Calculating ROI can be difficult, especially with intangible benefits like better decision-making.
Workaround:
- Develop a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis considering tangible and intangible benefits.
- Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) aligned with business objectives to measure the impact of the AI tools.
- Monitor and reassess the ROI over time, adjusting strategies as needed.
Adaptability to Changing Conditions
Challenge:
The supply chain operates in a dynamic environment with market fluctuations, regulatory changes, and unforeseen events. AI tools must be adaptable to these changing conditions.
Workaround:
- Integrating machine learning algorithms that consistently learn from new data will be beneficial.
- Regularly update the algorithms to adapt to changing market conditions.
- Implement agile development practices to facilitate quick adjustments and enhancements based on evolving business needs.
Lack of Industry Standards
Challenge:
The absence of standardized practices in AI for supply chain management can lead to interoperability issues and hinder collaboration between different stakeholders in the supply chain.
Workaround:
Collaborate with industry organizations to establish standards for data formats, communication protocols, and security measures. Engage in open dialogue with partners and suppliers to align on common practices and encourage the adoption of industry-wide standards.
Cost and Benefits of AI Tools designed for Supply Chain Visibility and Optimization
Costs of Creating and Using AI Tools:
1. Development Costs: The initial investment in developing Retail B2C Industry AI Tools involves expenses related to hiring skilled developers, data scientists, and AI specialists. Costs associated with acquiring or developing algorithms, designing user interfaces, and coding the toolset contribute to the development budget.
2. Integration Costs: Integrating AI tools with existing systems such as ERP, WMS, and databases requires specialized skills and may involve expenses for middleware solutions, APIs, and testing. The complexity of integration can impact both time and costs.
3. Training and Education Costs: Conducting comprehensive training programs for existing staff to familiarize them with the AI tools is a critical investment. Costs include training materials, sessions, and possibly hiring external trainers for specialized topics. Ongoing education to keep the workforce updated on the evolving technology adds to these expenses.
4. Maintenance and Updates: Continuous improvement necessitates ongoing maintenance and updates. This includes costs associated with monitoring tool performance, addressing issues, and updating algorithms or features to enhance effectiveness.
Benefits of Creating and Using AI Tools:
1. Improved Efficiency and Productivity: Retail B2C Industry AI Tools streamline supply chain operations, increasing efficiency and productivity. Automating route optimization, inventory management, and risk assessment reduces manual effort and accelerates decision-making processes.
2. Enhanced Visibility: The tools provide end-to-end visibility into the supply chain, offering real-time insights and analytics. This increased visibility enables proactive decision-making, better risk management, and prompt issue identification and resolution.
3. Cost Reduction: AI-powered optimization tools contribute to cost reduction by improving resource utilization, minimizing transportation expenses through route optimization, and reducing the impact of risks through proactive mitigation strategies. Efficient warehouse management also leads to cost savings in storage and fulfilment.
4. Accurate Demand Forecasting: The AI tools leverage advanced analytics to provide accurate demand forecasting. This results in optimized inventory levels, preventing overstocking or stockouts. Accurate forecasting enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring products are available when needed.
5. Supply Chain Resilience: AI tools contribute to building a resilient supply chain by providing the capability to adapt to changing conditions. Whether it’s market fluctuations, unexpected events, or alterations in consumer behaviour, the tools enable the supply chain to respond swiftly and maintain operational continuity.
6. Improved Customer Experience: By optimizing the supply chain, AI tools contribute to an improved customer experience. Timely deliveries, efficient return processes, and accurate order fulfilment enhance customer satisfaction, leading to repeat business and positive brand perception.
7. Strategic Decision-Making: The AI tools provide data-driven insights that empower strategic decision-making. With accurate and real-time information, organizations can make informed choices regarding supplier relationships, inventory investments, and overall supply chain strategies.
8. Competitive Advantage: Implementing AI tools for supply chain visibility and optimization gives companies a competitive edge. Efficient supply chain processes allow retail B2C businesses to respond to market changes and fulfil customer demands.
Conclusion
In conclusion, integrating Retail B2C Industry AI Tools for Supply Chain Visibility and Optimization marks a transformative leap forward for businesses seeking to thrive in today’s dynamic market. The challenges in developing, integrating, and utilizing these tools are undoubtedly present, but strategic workarounds and proactive measures can overcome these obstacles.
The costs of creating and implementing these tools, including development, integration, training, and ongoing maintenance, are substantial. However, the benefits are equally significant. Improved efficiency and productivity, enhanced visibility, accurate demand forecasting, and a resilient supply chain contribute to cost reduction and operational excellence. The positive impact extends to customer experience, strategic decision-making, and establishing a competitive advantage.
The technical intricacies of integrating AI tools with existing systems and ensuring data quality and accuracy underscore the need for a well-thought-out implementation strategy. User adoption and training programs play a pivotal role in overcoming the initial resistance to technology adoption and maximizing the benefits of these advanced tools.
While security concerns and the lack of industry standards present additional challenges, adherence to robust security measures and collaboration towards establishing standard industry practices can address these issues. The adaptability of AI tools to changing conditions, combined with a commitment to continuous learning, ensures that businesses stay ahead of evolving market dynamics.
Retail B2C Industry AI Tools for Supply Chain Visibility and Optimization offer a pathway to survive and thrive in an ever-evolving landscape. Investing in technology and committing to empowering the workforce with the necessary skills and knowledge are crucial to achieving sustainable growth and a competitive edge in the retail sector. As businesses embrace the transformative potential of these AI tools, the journey towards a more efficient, resilient, and customer-centric supply chain becomes a reality, shaping the future of retail in the digital age.
Related Articles
- AI Automation Tools in Brick-and-Mortar Retail Store
- AI Tools for Retail B2C Industry
- AI Tools for Customer Feedback and Support in Retail B2C
- AI Tools for Marketing and Advertising in Retail B2C Industry
- AI Tools for Fraud Prevention and Security in Retail B2C
- AI Tools for Sales and Conversion Optimization in the Retail B2C
- AI Tools for Customer Loyalty and Retention in Retail B2C
- AI Tools for Analytics and Reporting in Retail B2C Industry
- AI Tools for Product Management and Innovation in Retail
- AI Tools for Customer Experience and Engagement in Retail
- AI Tools for Inventory and Supply Chain Management for Retail
- AI in Retail Customer Experience